This document explain installation and test of the CogIMon Simulation Architecture (CoSimA) with support for IIT’s COMAN and the KUKA LWRIV+ robot. Please check back often as we continuously extend this documentation.
CoSiMA is modeled in a Cognitive Interaction Toolkit (CITk) distribution for easy replication. The CITk-based installer supports Ubuntu Trusty LTS 14.04 and LTS 16.04 64 Bit using Gazebo 7 and OROCOS-RTT 2.8.
The following commands add OSRF repositories for binary installations of recent Gazebo versions to your system.
Setup your computer to accept software from packages.osrfoundation.org.
Note: there is a list of available mirrors for this repository which could improve the download speed.
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo/ubuntu-stable `lsb_release -cs` main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gazebo-stable.list'
Setup keys.
wget http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo.key -O - | sudo apt-key add -
Update Package Cache.
sudo apt-get update
The following commands add ROS repositories for binary installation of ROS dependencies to your system. These are only required if you need the ROS interoperability features.
For example, if you want to use ROS Kinetic with CoSiMA as explained in the remainder of this tutorial, please execute the following instructions in a shell:
Setup your computer to accept software from packages.ros.org.
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
Setup keys.
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://ha.pool.sks-keyservers.net:80 --recv-key 421C365BD9FF1F717815A3895523BAEEB01FA116
Update Package Cache.
sudo apt-get update
Setup the CITk toolchain on your machine according to the instructions on this page
NOTE: If you are on Ubuntu Trusty, you need to source the ROS environment before starting the jenkins (./start_jenkins) in the linked tutorial. If you are on Ubuntu Xenial you don’t need to source the setup.bash
source /opt/ros/indigo/setup.bash
./start_jenkins
Clone the CITk recipe repository and checkout the CogIMon branch
mkdir -p $HOME/citk/dist && cd $HOME/citk/dist
git clone https://opensource.cit-ec.de/git/citk .
git checkout wip-cogimon
Issue the following command to get a list of platform requirements that shall be installed in the system prio to the source build of CoSiMA components:
$HOME/citk/jenkins/job-configurator --on-error=continue --cache-directory=/tmp/bg/ platform-requirements -p 'ubuntu xenial' distributions/cogimon-core-ros-nightly.distribution
NOTE: You may add --cache-directory=/tmp/bg/ to the build generator command in order to speed up repeated job generation as show in the following examples. You should replace -u USER and -p YOUR_PASSWORD with the Jenkins API token that can be retrieved from your Jenkins user profile or the password that you used during the Jenkins bootstrapping. These cpomments apply to all build generator commands in this tutorial.
Install the list of platform dependencies by copying the output of the generator command below “Found XX platform requirements…” as argument of an apt-get install command similar to the following example:
$ $HOME/citk/jenkins/job-configurator --on-error=continue --cache-directory=/tmp/bg/ platform-requirements -p 'ubuntu xenial' distributions/cogimon-core-ros-nightly.distribution
$ ...
$ Found 41 platform requirements for ubuntu xenial:
ant autoconf cmake g++ gcc git libboost-date-time-dev libboost-filesystem-dev \
libboost-program-options-dev libboost-regex-dev libboost-signals-dev \
libboost-system-dev libboost-test-dev libboost-thread-dev libeigen3-dev \
libgazebo7-dev libgtest-dev libomniorb4-dev libprotobuf-dev libprotobuf-java \
liburdfdom-dev libxml2-dev libyaml-cpp-dev make maven omniidl omniorb \
openjdk-8-jdk patch protobuf-compiler pylint python-dev python-gi \
python-minimal python-protobuf python-setuptools ros-kinetic-desktop ruby-dev \
tar unzip wget
$ sudo apt-get install ant autoconf cmake g++ gcc git libboost-date-time-dev
libboost-filesystem-dev libboost-program-options-dev libboost-regex-dev
libboost-signals-dev libboost-system-dev libboost-test-dev libboost-thread-dev
libeigen3-dev libgazebo7-dev libgtest-dev libomniorb4-dev libprotobuf-dev
libprotobuf-java liburdfdom-dev libxml2-dev libyaml-cpp-dev make maven omniidl
omniorb openjdk-8-jdk patch protobuf-compiler pylint python-dev python-gi
python-minimal python-protobuf python-setuptools ros-kinetic-desktop ruby-dev \
tar unzip wget
Initialize ROS dependency management by calling the following commands in a shell:
$ sudo rosdep init
$ rosdep update
Install the CoSiMA distribution of your choice.
In the following, we will install the CogIMon Core Simulation Distribution with ROS support, which is specified in the cogimon-core-ros-nightly.distribution file. If you do not need ROS support, you may install the CogIMon Core Simulation Distribution without ROS dependencies, which is available through the file cogimon-core-nightly.distribution. Just in case, please make sure that you checked and installed first the platform requirements of the respective distribution as explained in the previous step.
$HOME/citk/jenkins/job-configurator --on-error=continue --cache-directory=/tmp/bg/ generate -m toolkit -u YOUR_USERNAME -p YOUR_PASSWORD -D toolkit.volume=$HOME/citk/systems $HOME/citk/dist/distributions/cogimon-core-ros-nightly.distribution
In your local Jenkins build server trigger the cogimon-core-ros-nightly-toolkit-orchestration job (only possible after login). On the following page just hit hit build button.
Relax and grab a :coffee: …
Check for completion by verifying that all bullets are blue after the individual build has passed. Jenkins builds and installs the packages to the specified toolkit volume (see command line above).
The system can be manually tested in your Ubuntu environment with the following steps. The commands shown here assume that you execute them in a terminal using bash.
Source the particular script, which you’ll find in your $prefix which is $HOME/citk/systems/cogimon-core-ros-[trusty]-nightly.
source $HOME/citk/systems/cogimon-core-ros-nightly/bin/setup-cogimon-env.sh
Start the RSB Server process
source $HOME/citk/systems/cogimon-core-nightly/bin/setup-cogimon-env.sh
rsb0.17 server
You should see some output confirming that the server has started.
Start the RTT Deployer console
source $HOME/citk/systems/cogimon-core-nightly/bin/setup-cogimon-env.sh
deployer-gnulinux
You should get a shell-style prompt, which allows you to interact with the RTT environment.
Load and start the required CoSimA components
Please type within the deployer-console (replace $HOME with the expanded installation prefix, e.g. /home/$YOUR_USRNAME/):
loadService("this","scripting")
scripting.runScript("$HOME/citk/systems/cogimon-core-nightly/etc/cogimon-scenarios/scenario-coman/coman_bring_up_rsb.ops")
You should see quite some output in the deployer that you may ignore for now.
Start an RSB Logger process (optional)
source $HOME/citk/systems/cogimon-core-nightly/bin/setup-cogimon-env.sh
rsb0.17 logger socket:/
You should see a data stream that sends joint feedback with 100Hz.
Start the Gazebo client process
source $HOME/citk/systems/cogimon-core-nightly/bin/setup-cogimon-env.sh
gzclient
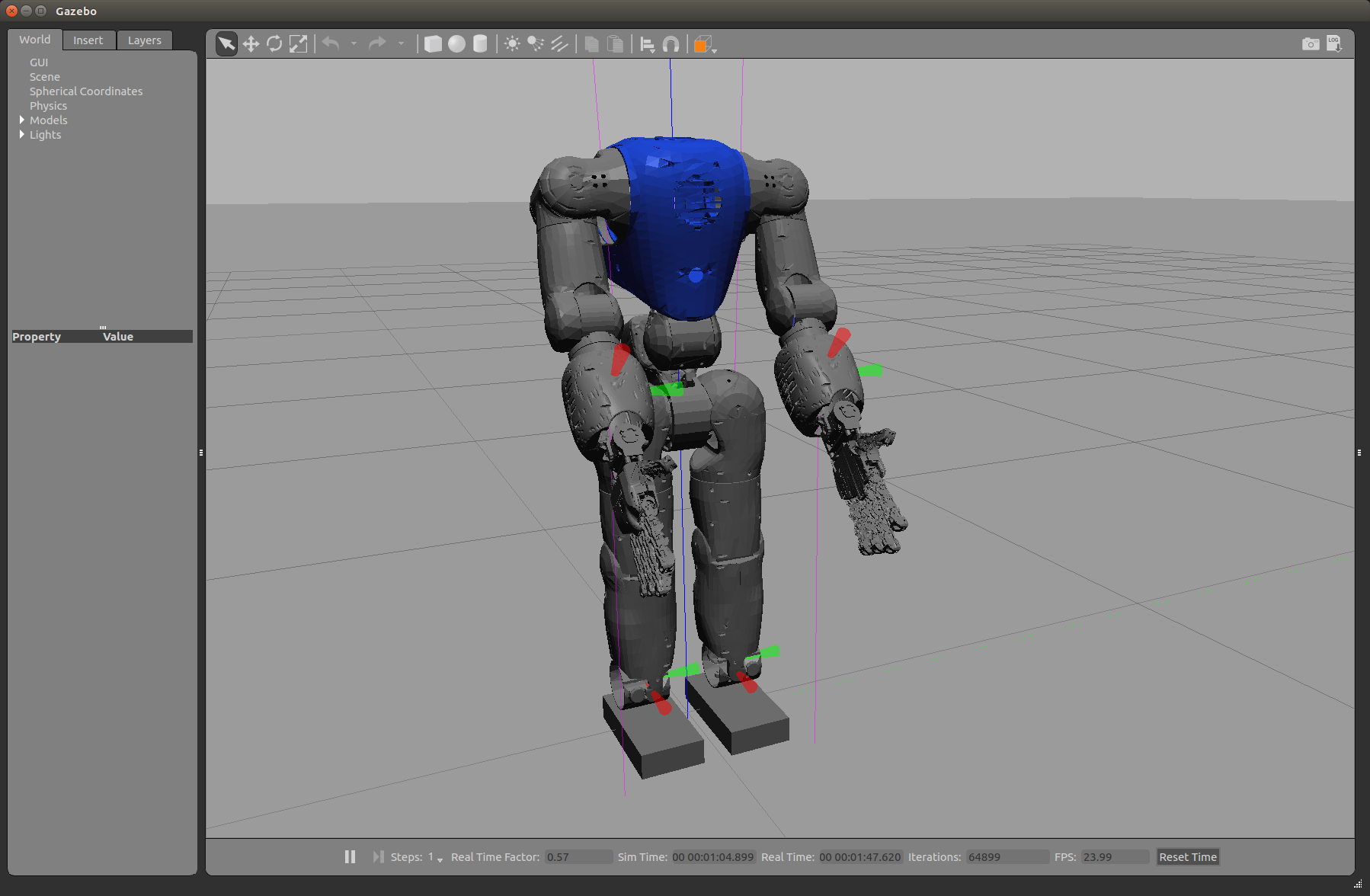
You should see the robot standing in the center of the simulated Gazebo world similar to the following screenshot: